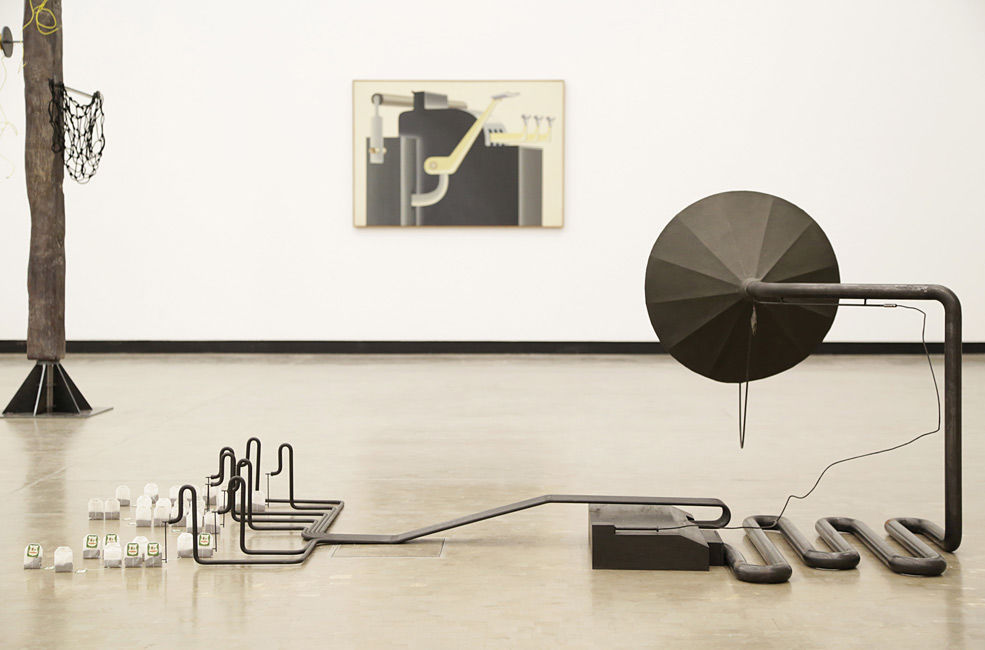

Installation view The Promise of Total Automation. Image Kunsthalle Wien
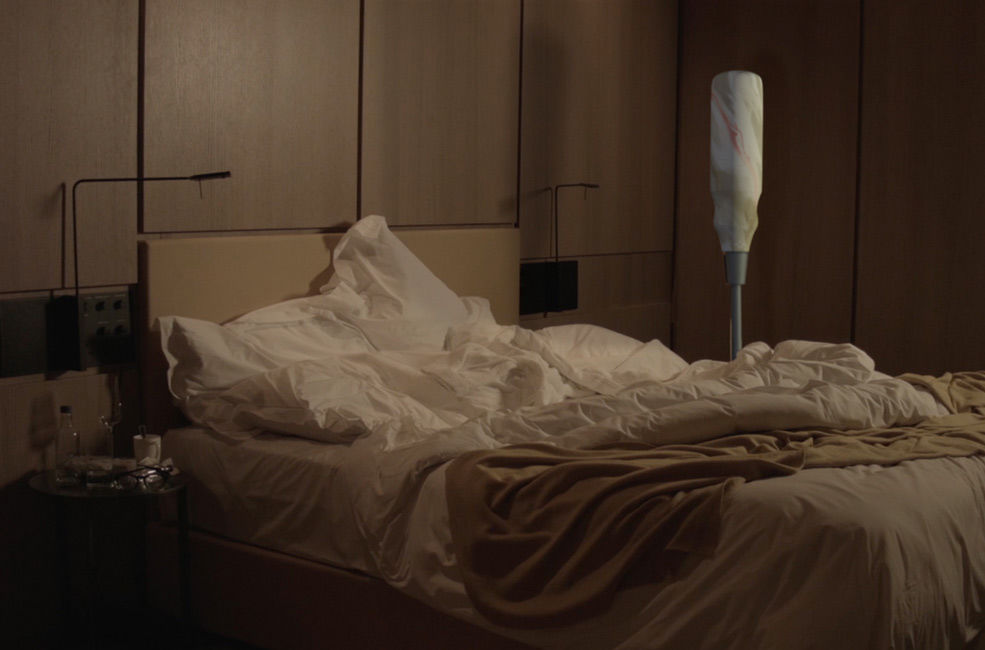

Cécile B. Evans, How happy a Thing Can Be, 2014. Image Kunsthalle Wien
The word ‘automation’ is appearing in places that would have seemed unlikely to most people less than a decade ago: journalism, art, design or law. Robots and algorithms are being increasingly convincing at doing things just like humans. And sometimes even better than humans.
The Promise of Total Automation, an exhibition recently opened at Kunsthalle Wien in Vienna, looks at our troubled relationship with machines. Technical devices that were originally designed to serve and assist us and are now getting smarter and harder to control and comprehend. Does their growing autonomy mean that the machines will one day overpower us? Or will they remain our subservient little helpers, our gateway to greater knowledge and sovereignty?
The “promise of total automation” was the battle cry of Fordism. What we nowadays call “technology” is an already co-opted version of it, being instrumentalised for production, communication, control and body-enhancements, that is for a colonisation and rationalisation of space, time and minds. Still technology cannot be reduced to it. In the exhibition, automation, improvisation and sense of wonder are not opposed but sustain each other. The artistic positions consider technology as complex as it is, animated at the same time by rational and irrational dynamics.
The Promise of Total Automation is an intelligent, inquisitive and engrossing exhibition. Its investigation into the tensions and dilemmas of human/machines relationship explore themes that go from artificial intelligence to industrial aesthetics, from bio-politics to theories of conspiracy, from e-waste to resistance to innovation, from archaeology of digital communication to utopias that won’t die.
The show is dense in information and invitations to ponder so don’t forget to pick up one of the free information booklet at the entrance of the show. You’re going to need it!
A not-so-quick walk around the show:
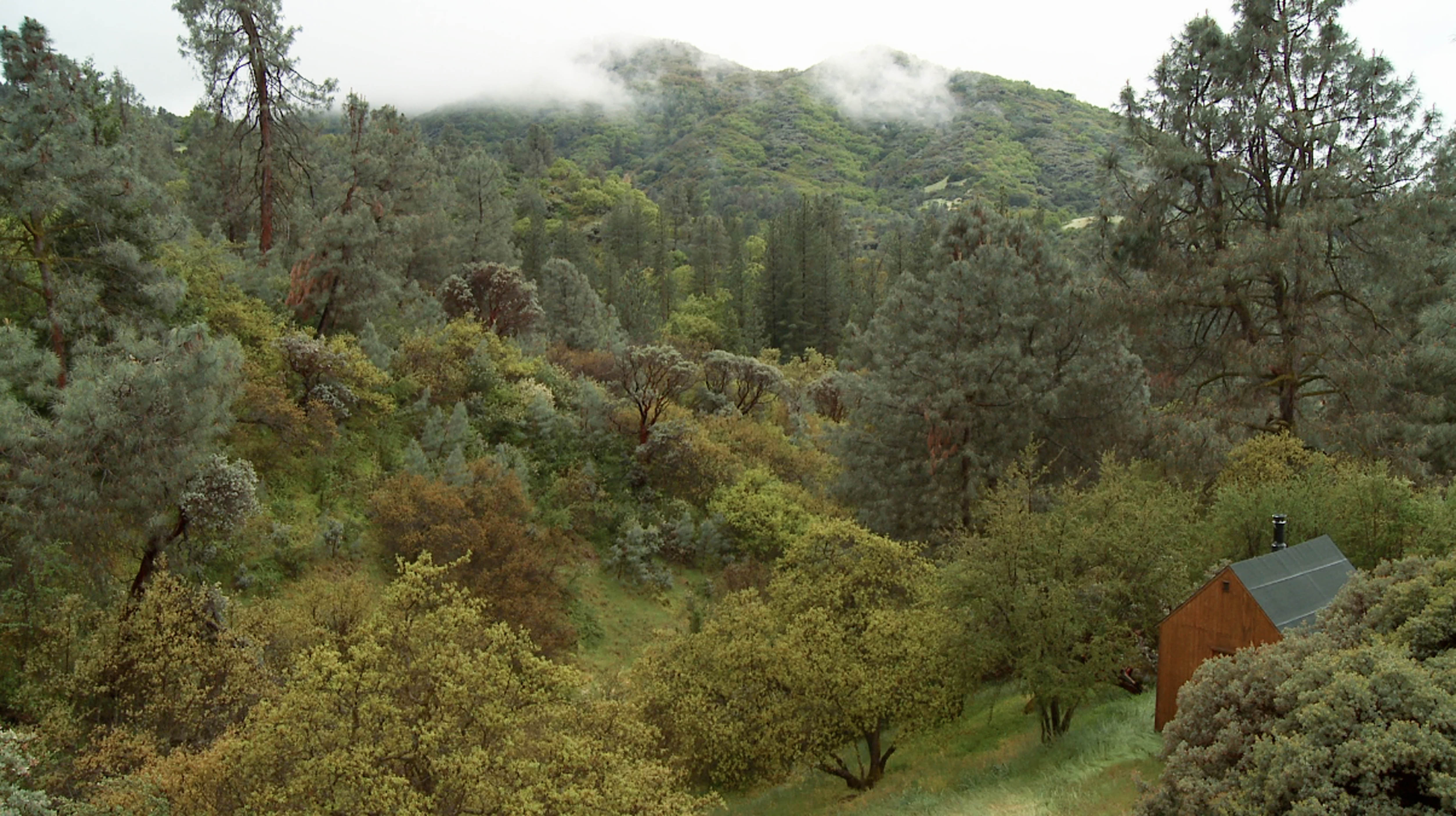


James Benning, Stemple Pass, 2012
James Benning‘s film Stemple Pass is made of four static shots, each from the same angle and each 30 minutes long, showing a cabin in the middle of a forest in spring, fall, winter and summer. The modest building is a replica of the hideout of anti-technology terrorist Ted Kaczynski. The soundtrack alternates between the ambient sound of the forest and Benning reading from the Unabomber’s journals, encrypted documents and manifesto.
Kaczynski’s texts hover between his love for nature and his intention to destroy and murder. Between his daily life in the woods and his fears that technology is going to turn into an instrument that enables the powerful elite to take control over society. What is shocking is not so much the violence of his words because you expect them. It’s when he gets it right that you get upset. When he expresses his distrust of the merciless rise of technology, his doubts regarding the promises of innovation and it somehow makes sense to you.
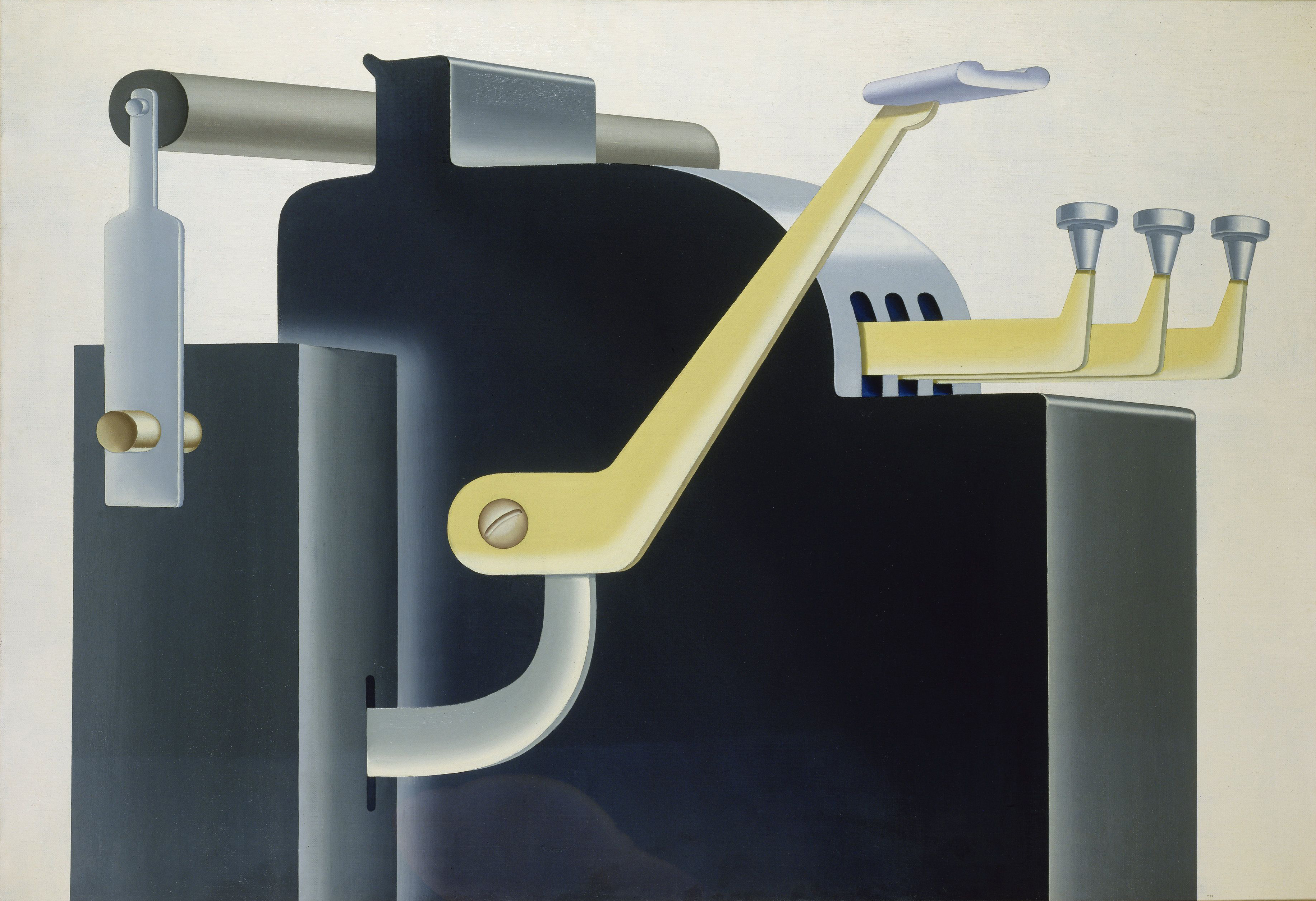

Konrad Klapheck, Der Chef, 1965. Photo: © Museum Kunstpalast – ARTOTHEK
Konrad Klapheck’s paintings ‘portray’ devices that were becoming mainstream in 1960s households: vacuum cleaner, typewriters, sewing machines, telephones, etc. In his works, the objects are abstracted from any context, glorified and personified. In the typewriter series, he even assigns roles to the objects. They are Herrscher (ruler), Diktator, Gesetzgeber (lawgiver) or Chef (boss.) These titles allude to the important role that the instruments have taken in administrative and economic systems.
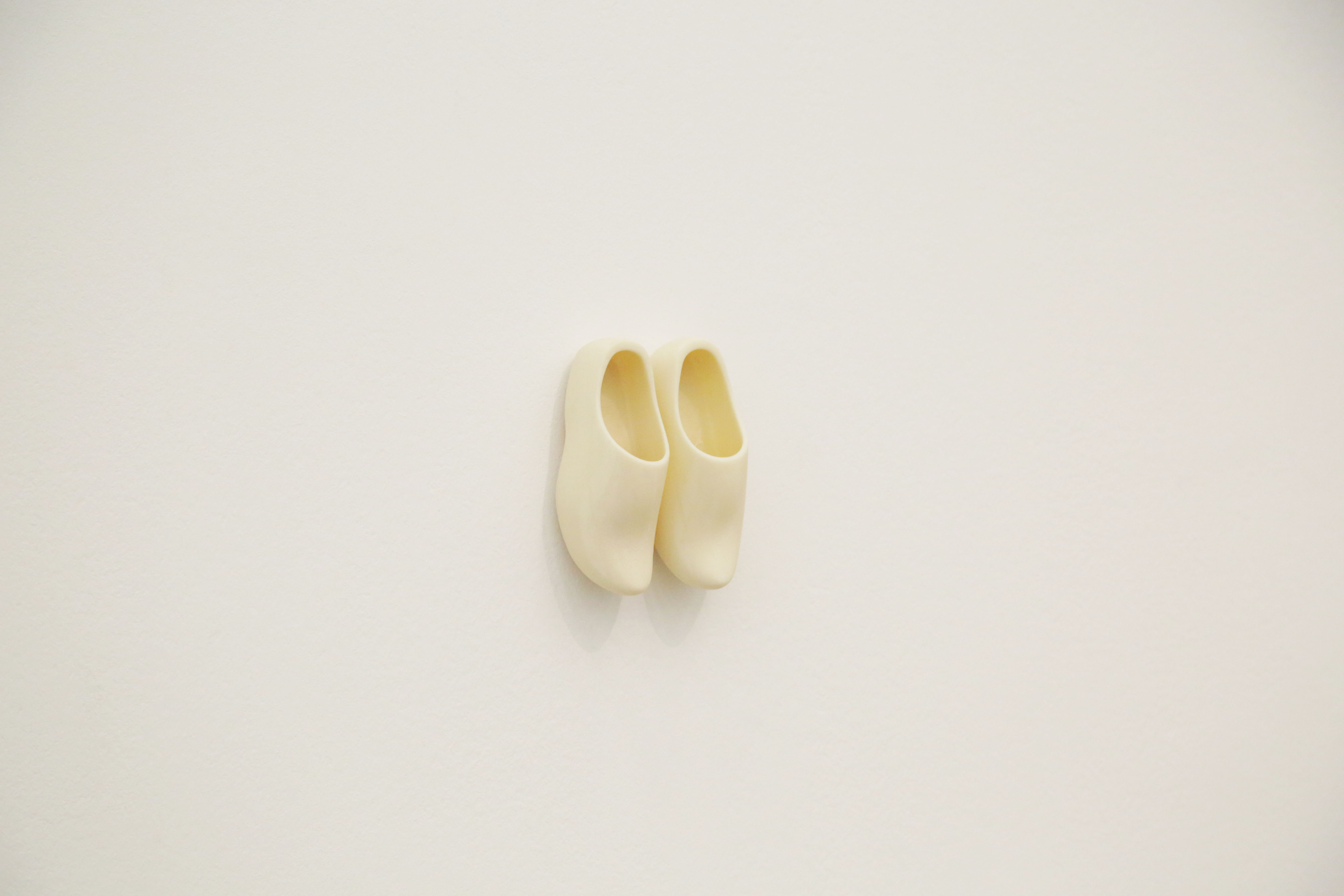

Tyler Coburn, Sabots, 2016, courtesy of the artist, photo: David Avazzadeh
This unassuming small pair of 3D-printed clogs alludes to the workers struggles of the Industrial Revolution. The title of the piece, Sabots, means clogs in french. The word sabotage allegedly comes from it. The story says that when French farmers left the countryside to come and work in factories they kept on wearing their peasant clogs. These shoes were not suited for factory works and as a consequence, the word ‘saboter’ came to mean ‘to work clumsily or incompetently’ or ‘to make a mess of things.’ Another apocryphal story says that disgruntled workers blamed the clogs when they damaged or tampered machinery. Another version saw the workers throwing their clogs at the machine to destroy it.
In the early 20th century, labor unions such as the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) advocated withdrawal of efficiency as a means of self-defense against unfair working conditions. They called it sabotage.
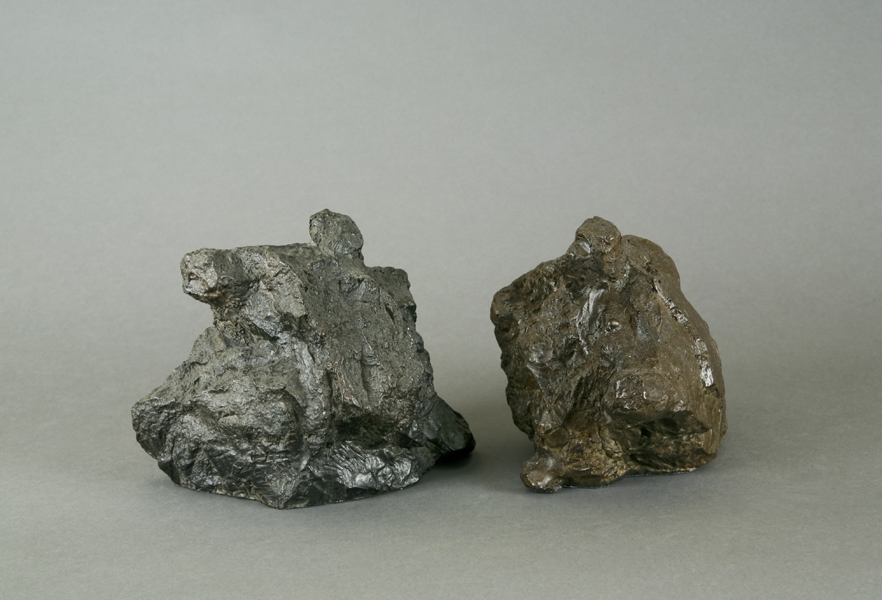

Tyler Coburn, Waste Management, 2013-15
Tyler Coburn contributed another work to the show. Waste Management looks like a pair of natural stones but the rocks are actually made out of electronic waste, more precisely the glass from old computer monitors and fiber powder from printed circuit boards that were mixed with epoxy and then molded in an electronic recycling factory in Taiwan. The country is not only a leader in the export of electronics, but also in the development of e-waste processing technologies that turn electronic trash into architectural bricks, gold potassium cyanide, precious metals—and even artworks such as these rocks. Coburn bought them there as a ready made. They evoke the Chinese scholar’s rocks. By the early Song dynasty (960–1279), the Chinese started collecting small ornamental rocks, especially the rocks that had been sculpted naturally by processes of erosion.
Coburn’s rocks are thus artificial objects that crave an aesthetic value that can only come from natural objects.
Accompanying these objects is a printed broadsheet which narrates the circulation and transformation of a CRT monitor into the stone artworks. The story follows from the “it-narrative” or novel of circulation, a sub-genre of 18th Century literature, in which currencies and commodities narrated their circulation within a then-emerging global economy.
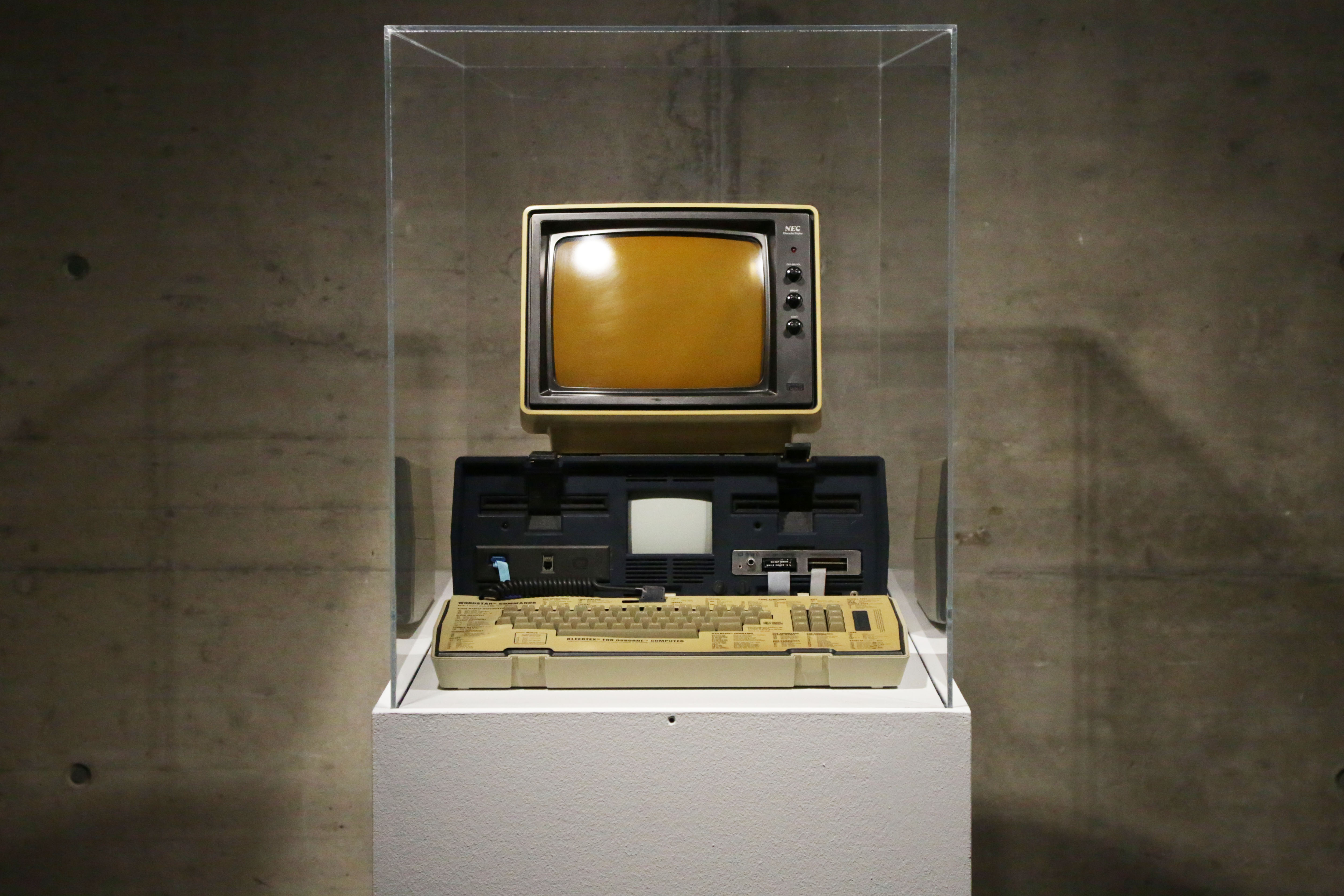

Osborne & Felsenstein, Personal Computer Osborne 1a and Monitor NEC, 1981, Loan Vienna Technical Museum, photo: David Avazzadeh
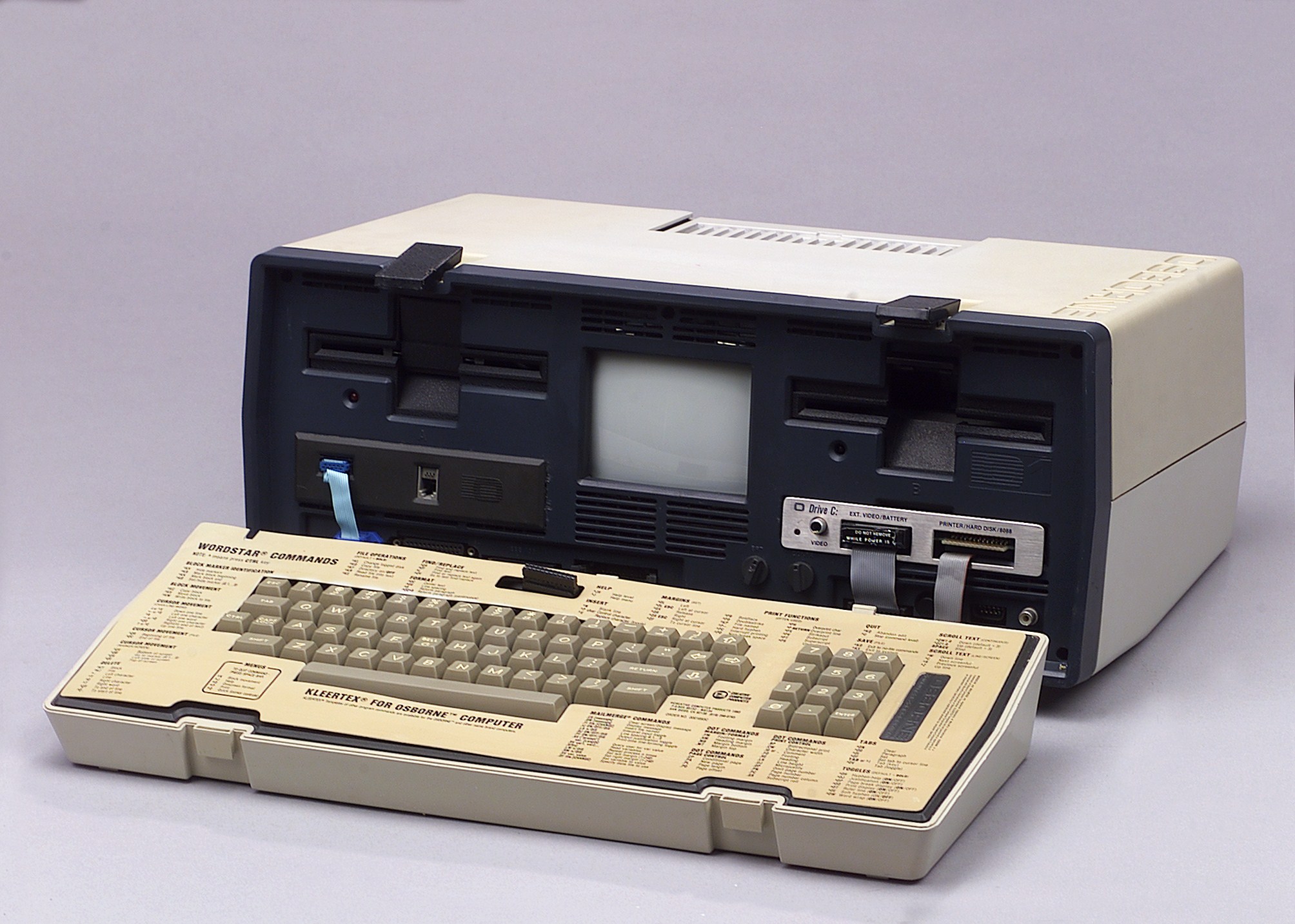

Adam Osborne and Lee Felsenstein, Personal Computer Osborne 1a, 1981, Courtesy Technisches Museum, Wien
Several artifacts ground the exhibition into the technological and cultural history of automation: A mechanical Jacquard loom, often regarded as a key step in the history of computing hardware because of the way it used punched cards to control operations. A mysterious-looking arithmometer, the first digital mechanical calculator reliable enough to be used at the office to automate mathematical calculations. A Morse code telegraph, the first invention to effectively exploit electromagnetism for long-distance communication and thus a pioneer of digital communication. A cybernetic model from 1956 (see further below) and the first ‘portable’ computer.
Released in 1981 by Osborne Computer Corporation, the Osborne 1 was the first commercially successful portable microcomputer. It weighed 10.7 kg (23.5 lb), cost $1,795 USD, had a tiny screen (5-inch/13 cm) and no battery.
At the peak of demand, Osborne was shipping over 10,000 units a month. However, Osborne Computer Corporation shot itself in the foot when they prematurely announced the release of their next generation models. The news put a stop to the sales of the current unit, contributing to throwing the company into bankruptcy. This has comes to be known as the Osborne effect.
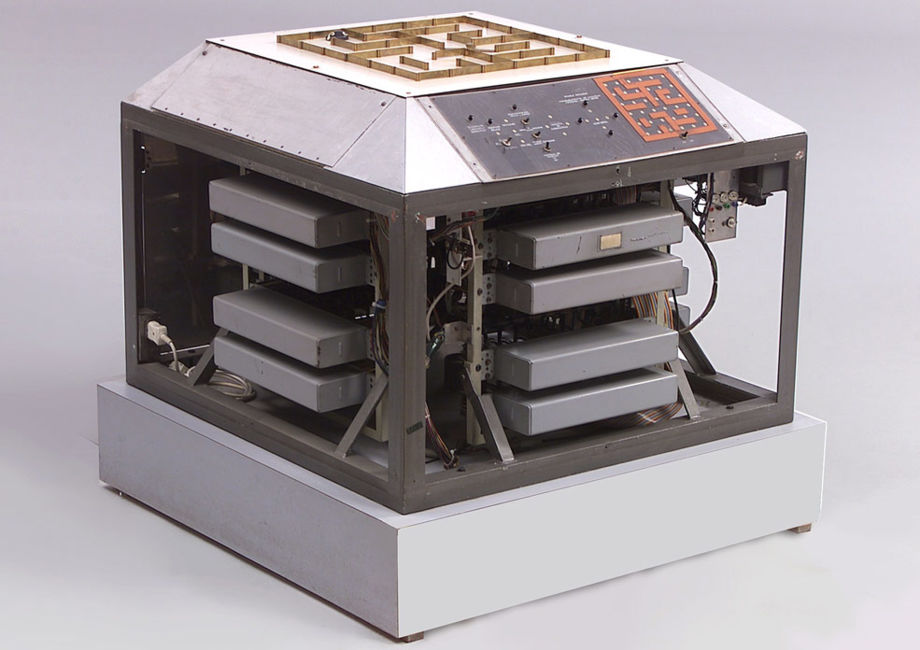
Kybernetisches Modell Eier: Die Maus im Labyrinth (Cybernetics Model Eier: The Mouse in the Maze), 1956. Image Kunsthalle Wien
Around 1960, scientists started to build cybernetic machines in order to study artificial intelligence. One of these machines was a maze-solving mouse built by Claude E. Shannon to study the labyrinthian path that a call made using telephone switching systems should take to reach its destination. The device contained a maze that could be arranged to create various paths. The system followed the idea of Ariadne’s thread, the mouse marking each field with the path information, like the Greek mythological figure did when she helped Theseus find his way out of the Minotaur’s labyrinth. Richard Eier later re-built the maze-solving mouse and improved Shannon’s method by replacing the thread with two two-bits memory units.
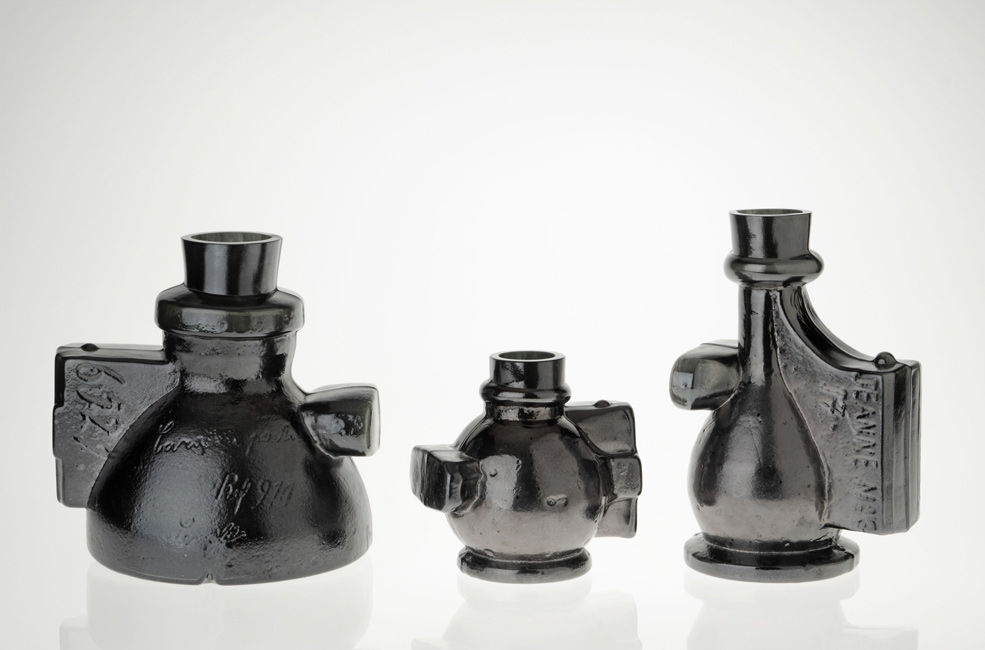

Régis Mayot, JEANNE & CIE, 2015. Image Kunsthalle Wien
In 2011, the CIAV (the international center for studio glass in Meisenthal, France) invited Régis Mayot to work in their studios. The designer decided to explore the moulds themselves, rather than the objects that were produced using them. By a process of sand moulding, the designer revealed the mechanical beauty of some of these historical tools, producing prints of a selection of moulds that were then blown by craftsmen in glass.
Jeanne et Cie (named after one of the moulds chosen by the designer) highlights how the aesthetics of objects are the result of the industrial instruments and processes that enter into their manufacturing.
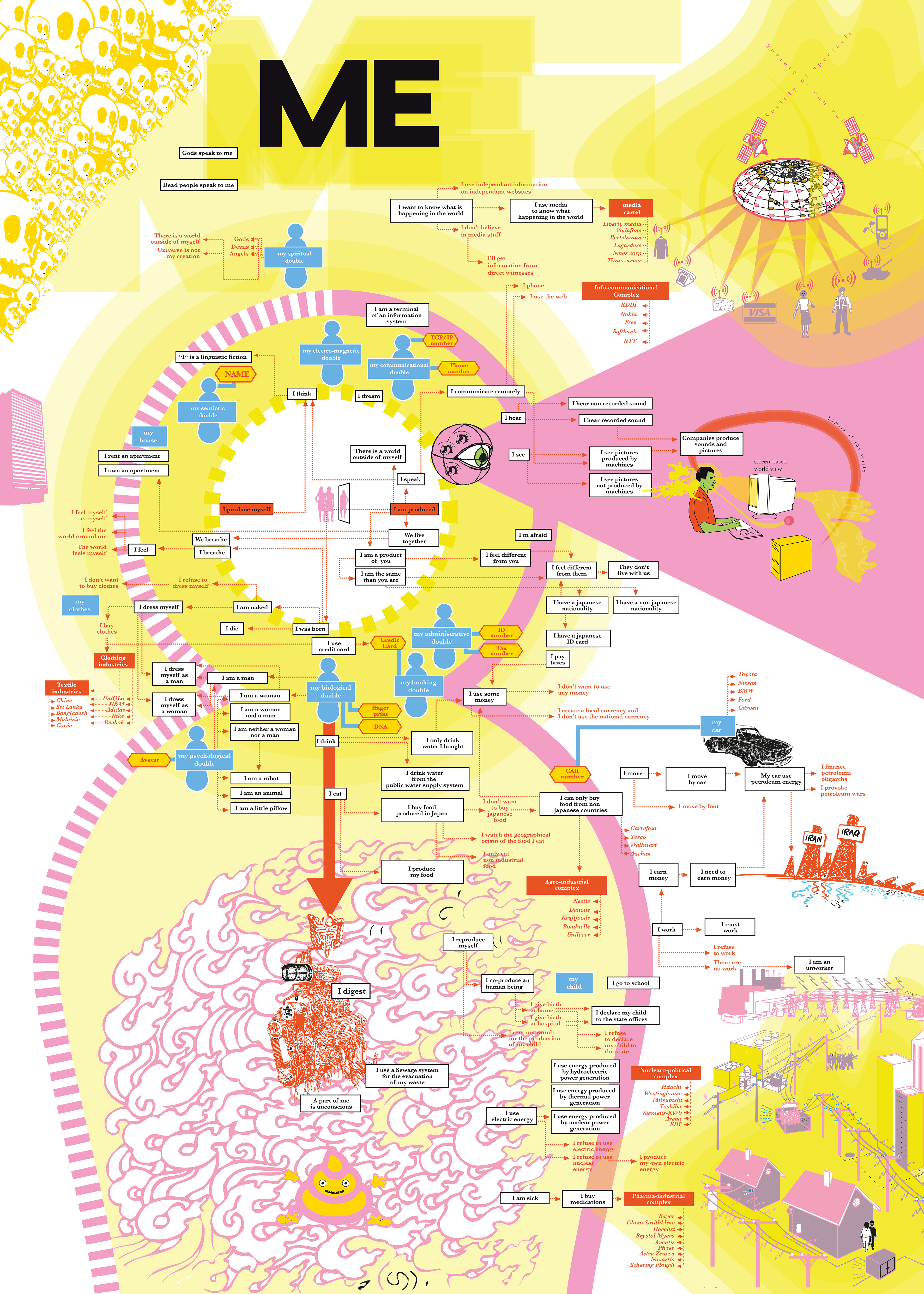
Bureau d’études, ME, 2013, © Léonore Bonaccini and Xavier Fourt

Bureau d’Etudes, Electromagnetic Propaganda, 2010
The exhibition also presented a selection of Bureau d´Études‘ intricate and compelling cartographies that visualize covert connections between actors and interests in contemporary political, social and economic systems. Because knowledge is power, the maps are meant as instruments that can be used as part of social movements. The ones displayed at Kunsthalle Wien included the maps of Electro-Magnetic Propaganda, Government of the Agro-Industrial System and the 8th Sphere.
Mark Leckey, Pearl Vision, 2012
I fell in love with Mark Leckey‘s video. So much that i’ll have to dedicate another post to his work. One day.

David Jourdan, Untitled, 2016, © David Jourdan
David Jourdan’s poster alludes to an ad in which newspaper Der Standard announced that its digital format was ‘almost as good as paper.’
More images from the exhibition:

Magali Reus, Leaves, 2015
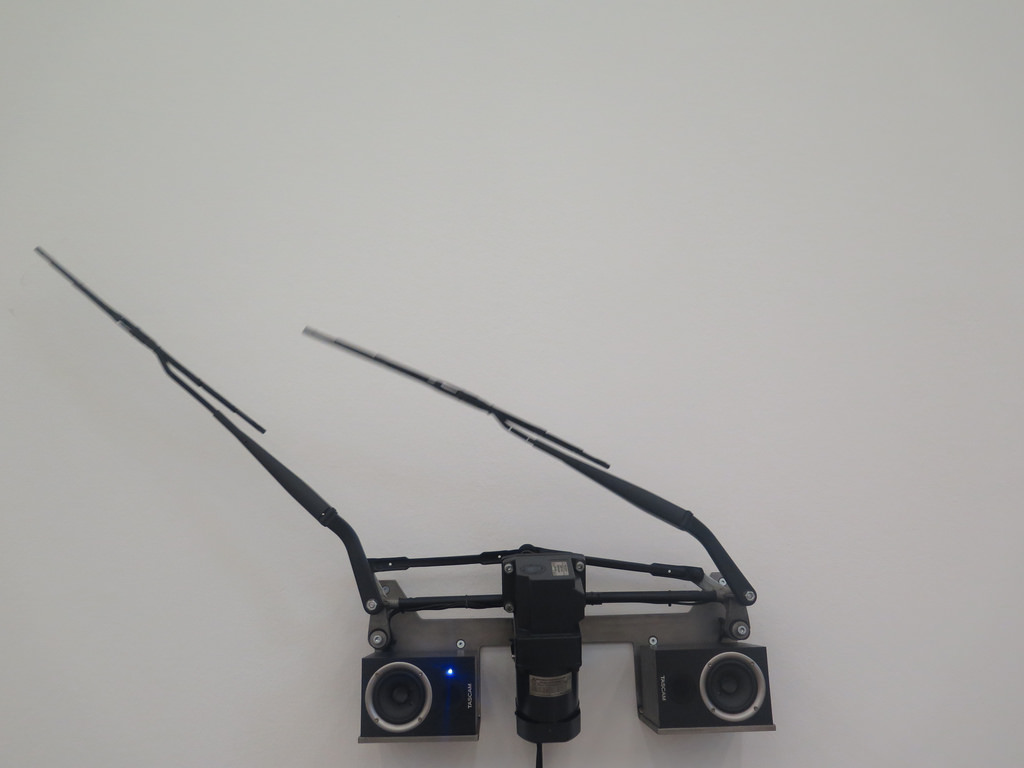

Thomas Bayrle, Kleiner koreanischer Wiper
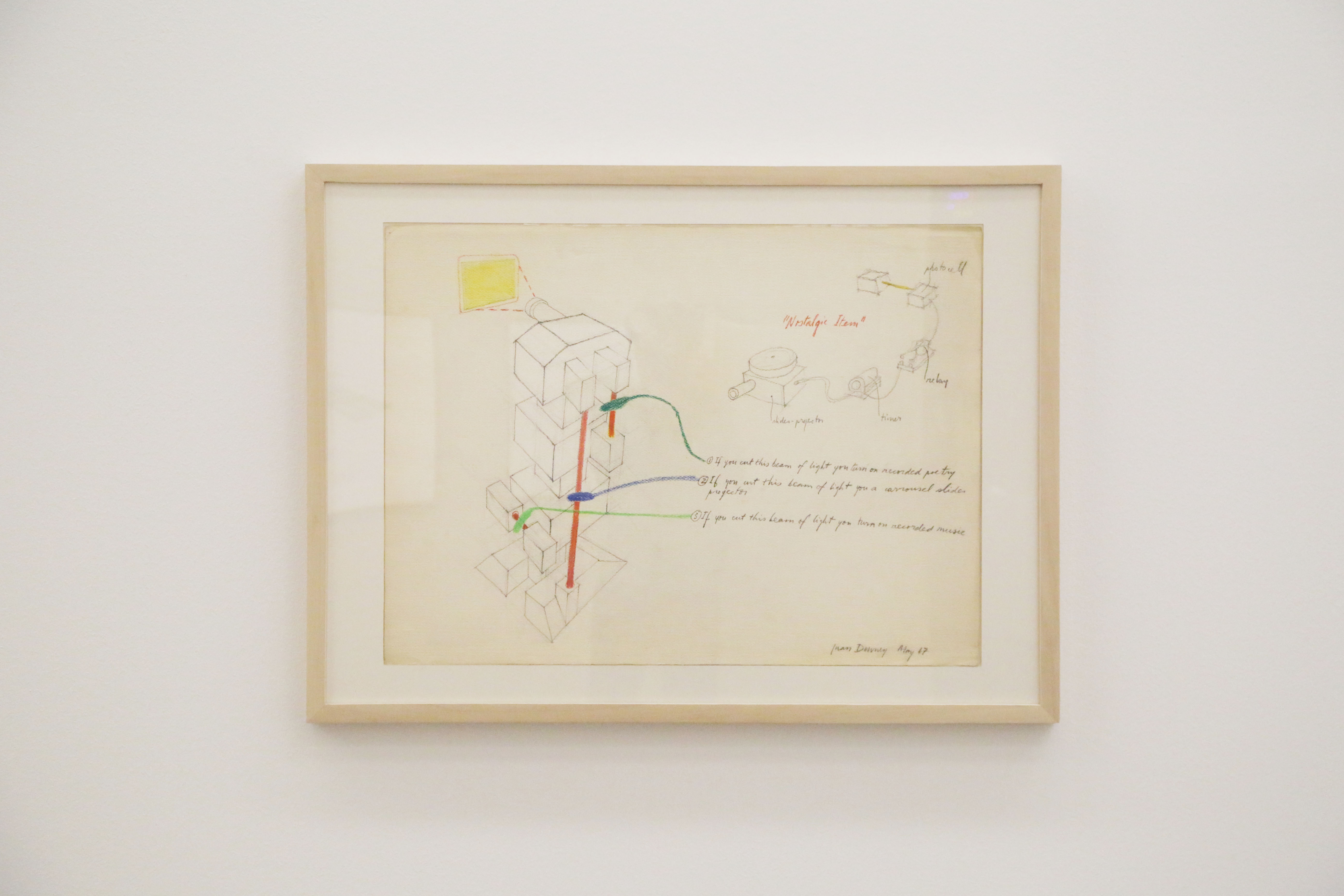
Juan Downey, Nostalgic Item, 1967, Estate of Joan Downey courtesy of Marilys B. Downey, photo: David Avazzadeh
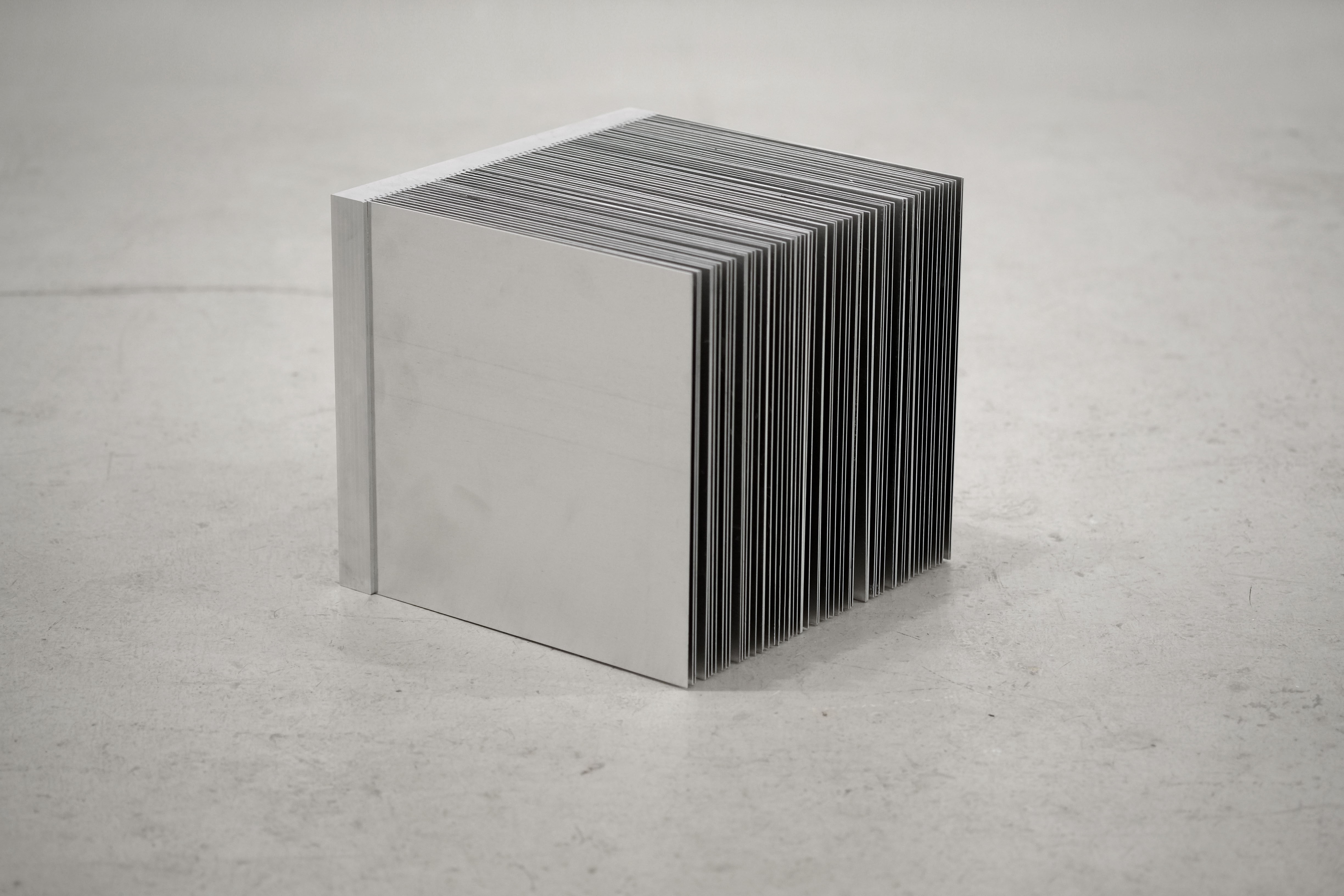
Judith Fegerl, still, 2013, © Judith Fegerl, Courtesy Galerie Hubert Winter, Wien
Wesley Meuris, Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering, 2014. Image Kunsthalle Wien

Installation view The Promise of Total Automation. Image Kunsthalle Wien

Installation view. Image Kunsthalle Wien

Installation view. Image Kunsthalle Wien
More images on my flickr album.
Also in the exhibition: Prototype II (after US patent no 6545444 B2) or the quest for free energy.
The Promise of Total Automation was curated by Anne Faucheret. The exhibition is open until 29 May at Kunsthalle Wien in Vienna. Don’t miss it if you’re in the area.







